Hello friends, Today in this topic we are going to talk about what is a taper and how many types of taper are there?
At the end of this topic, we will also know how to calculate a taper ratio and taper angle? Taper means short or thin towards one end. It also means a gradual decrease in the width or thickness of a long object.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Taper?
Taper, also known as taper conicity, refers to the consistent and gradual increase or decrease in the diameter of a cylindrical workpiece. The concept of taper operates based on the principles of trigonometry.
L = Length of the taper
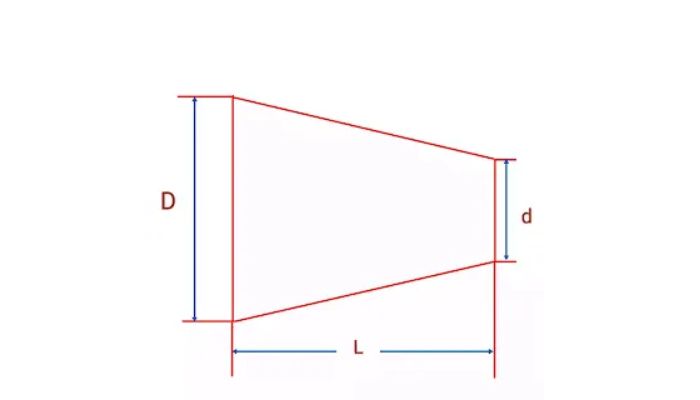
To gain a comprehensive understanding of taper types, it is essential to first acquaint ourselves with the methods of specifying taper. This foundational knowledge will provide a solid basis for a thorough comprehension of the various types of tapers.
Methods of Specified Taper
A taper can be specified in the following ways:
- Taper in Degree
- Taper in Inch
- Taper in Foot
- Taper in Metric
- Standard Taper Number
- Taper by Symbol
Taper in Degree
In this method, the taper is expressed in degree.
Like 60°, 3°,30°, etc.
Taper in Inch
In inch systems, tapers are expressed in a taper per inch.
Like 0.0208″.
Taper in Foot
In foot systems, tapers are expressed in a taper per foot.
Like 5/8′.
Taper in Metric
Metric tapers are represented in the ratio of 1 mm per unit length.
For example in a 1: 20 taper the diameter will change 1 mm per 20 mm length.
Standard Taper Number
According to standard taper, numbers taper can be specified as their standard number
For Example, Morse taper specified in MT 0 to MT 7.
Read also: Try Square: Parts, Types, Grades, Checking Accuracy, Uses
Taper by Symbol
In this method taper is expressed by a symbol for example taper is denoted by K.
Types of Taper
A taper can be classified into three categories:
- According to Class
- According to Use
- According to Size
According to Class
According to class, there are two types of taper:
- Self Holding Taper
- Quick Releasing Taper
Self Holding Taper
In this type of taper, the taper angle is kept at less than 3°.
In that taper does not require any other locking device to hold the assembled component.
It is also called a slow taper.
Quick Releasing Taper
Due to the high Taper Angle, they require a locking device to clamp.
They have a Taper ratio of 7:24.
According to Use
According to uses are two types of taper
- Internal Taper
- External Taper
Internal Taper
The taper given on the inner surface of a cylindrical job or a workpiece is called an internal taper.
External Taper
The taper given on the outer surface of a cylindrical job or a workpiece is called an external taper.
According to Size
According to size, there are the following types of taper:
- Morse Taper
- Metric Taper
- Jarno Taper
- Brown and Sharpe Taper
- Standard Pin Taper
- Jacobs Taper
Morse Taper
Morse Taper is a self holding type taper and it is available in an 8 size from MT 0 to MT 7.
The taper ratio of morse taper is found at 1:10 and its included angle is available in 3° or 5/8 inch/foot.
Morse taper is mostly used in lathe machines ds nose spindle, drill shank, arbor, etc.
Metric Taper
Jarno Taper
Jarno taper is also the self holding type of taper and is available in 20 sizes from 01 to 20.
The taper ratio of the Jarno taper is 1:20 and its included angle is available at 0.6 inches/foot.
It is mostly used in die marking machines.
Brown and Sharpe Taper
The Brown and Sharpe taper is characterized as a taper that serves both self-holding and quick-releasing functions. It encompasses 18 sizes in the self-holding category and 9 sizes in the quick-releasing category.
Within the self-holding designation, the Brown and Sharpe taper ranges from BS 1 to BS 18, whereas the quick-releasing subset spans from 4 to 12.
With a taper ratio of 1:20, the Brown and Sharpe taper exhibits a specific included angle, exemplified by the value of 0.5161 inches per foot for BS 10. For all other taper types within this category, the included angles are standardized at 1/2 inch per foot.
This versatile taper finds its application in the spindle and arbor components of milling machines, showcasing its adaptability and utility in machining operations.
Standard Pin Taper
The standard pin taper is characterized as a self-holding taper, offering stability without the need for additional locking mechanisms.
With a taper ratio of 1:50 in metric and 1:48 in British standards, the standard pin taper demonstrates adaptability to different measurement systems. The included angle for this taper is consistent at 1/4 inch per foot.
This taper is commonly employed in various applications, such as clamp devices and tapered pins, showcasing its versatility in accommodating diverse mechanical needs.
Jacobs Taper
Jacobs taper is mostly used in drill press chuck, arbor, etc.
How to Calculate a Taper Ratio and Taper Angle?
For calculating the taper ratio there are following formula applied:
Taper Rati
K = D-d/L
Where,
K = Taper Ratio
D = Larger diameter of the taper
d = Smaller diameter of the taper
L = Length of the taper
Taper Angle
Tan θ = D-d/2L
θ = tan-1 (D-d/2L)
Where,
D = Larger diameter of the taper
d = Smaller diameter of the taper
L = Length of the taper
For Example,
For a taper with a large diameter of 40 mm, a small diameter of 30 mm, and a total length of 20 mm, the taper ratio is \(0.5\), and the taper angle is approximately \(14.04^\circ\).
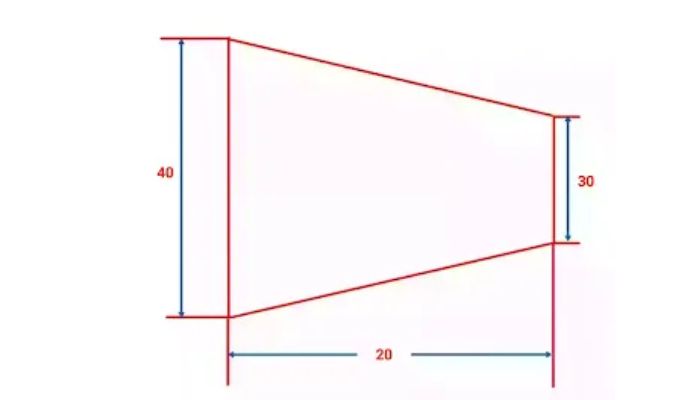
Taper Ratio = (40 – 30)/20
= 10/20
= 1/2
That means the taper ratio is 1:2
Taper Angle
tan θ = (40-30)/(2×20)
θ = tan-1(10/40)
= 14.03°
So friends here I discussed types of taper according to their class, size, and uses briefly. And also known how to calculate taper ratio and taper angle?
Read also: Are PET Bottles Safe for us and the environment?
I hope you clearly understand all aspects related to taper.
Thank You.